Transform
Transform
Use the transform method to transform the x, y and/or z coordinates of the points on the grid.
The first argument is the transform function, which will have as it's arguments the current point and it's col, row (and layer for 3D grids) index. Here you can mutate the point's x, y and z position and must return the mutated point.
Some examples:
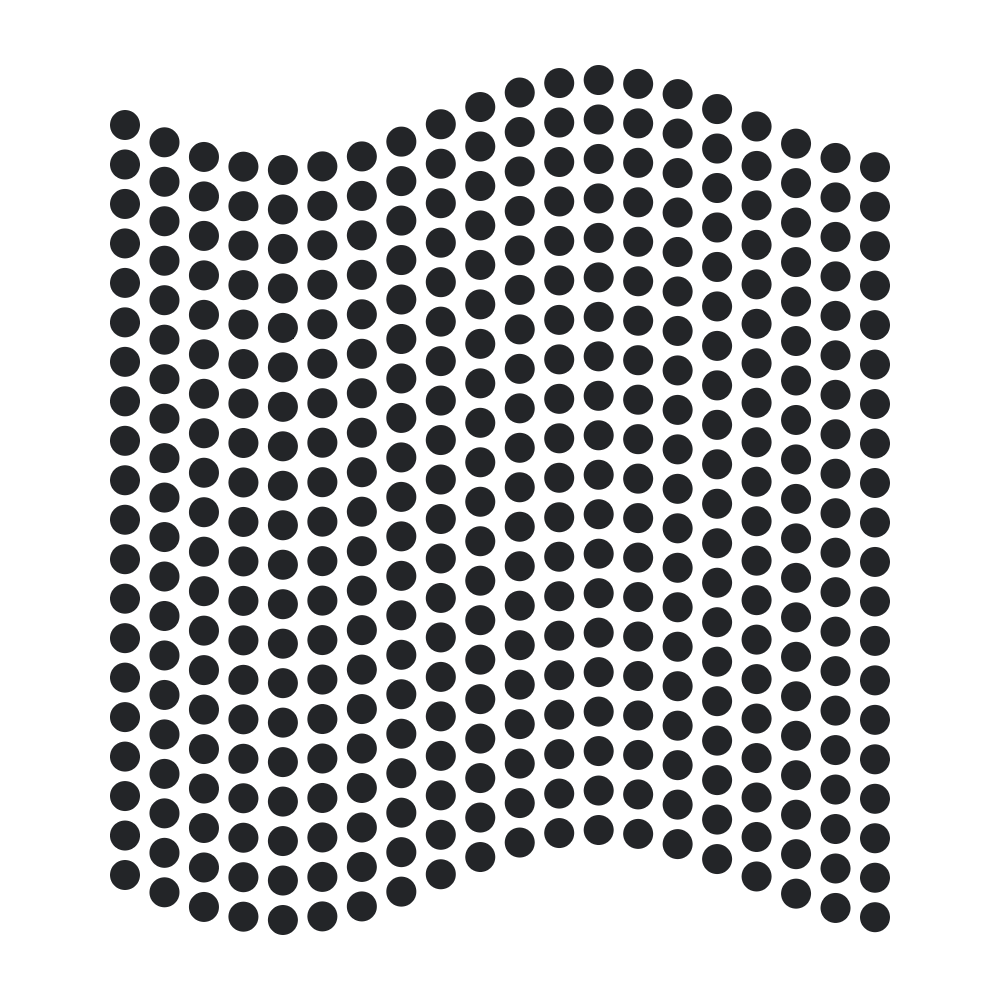
// Make the points on the grid follow a sine wave pattern
const grid = createGrid({ cols: 20, rows: 20, height: 500, width: 500 })
const transformSineWave = (point) => {
point.y += Math.sin(point.x * 0.015) * 30;
return point;
}
grid.transform(transformSineWave)
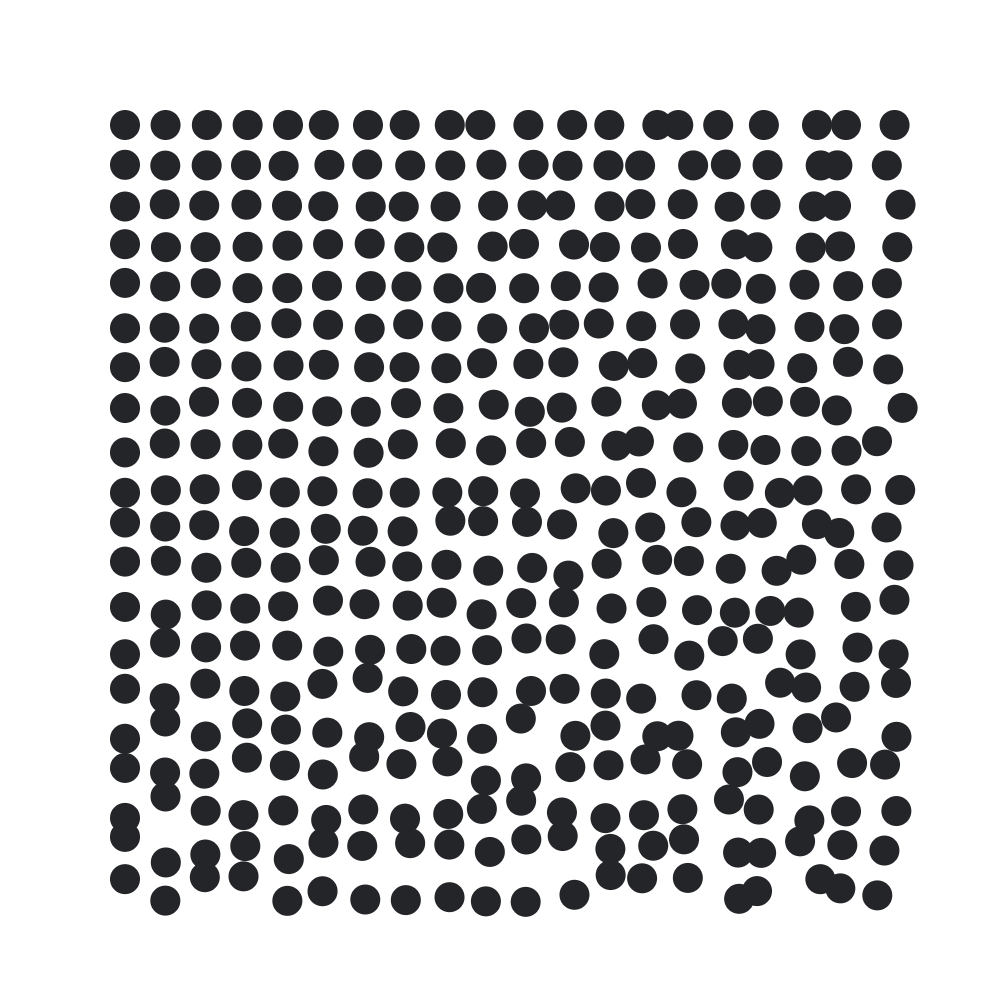
// increase the scattering of points from top-left to bottom-right
const increasedScatter = (point, col, row) => {
point.x += Math.random() * col;
point.y += Math.random() * row;
return point;
}
grid.transform(increasedScatter)

Translate
Use the translate method to translate a grid by a x and y coordinate. For example to translate a grid by 10 pixels horizontally and 20 pixels vertically:
grid.translate(10, 20);
to visualize this:
grid.every((point) => whiteDot(point.x, point.y));
grid.translate(10, 20);
grid.every((point) => orangeCircle(point.x, point.y));

To translate a grid on the z-axis, 3D grids implement the translate method using the 3rd z argument.
my3dGrid.translate(10, 20, 30);
grid.translate(3, 5, 8)is a shorthand for the.transformfunction:grid.transform(point => {
point.x += 3;
point.y += 5;
point.z += 8;
return point;
})
Chaining
To write a sequence of Grid methods more compact, you chain grid methods after another. For example to translate a grid two times and draw it right afterwards:
grid.translate(10, 20);
.translate(30, 0);
.every(point => ...);
Currently following methods support chaining:
- every
- transform
- translate